Bolt Business Model | How Does Bolt Make Money
Ever wondered how apps like Bolt have changed the way we move around cities? Today, you can book a ride, rent a scooter, or order food, all from one app. Pretty cool, right? Bolt is one of the biggest names in the ride-hailing world, giving tough competition to giants like Uber.
In this blog, we’ll break down the Bolt business model and see exactly how Bolt makes money. If you’re thinking about launching your own taxi app or dreaming of building a successful Bolt clone, keep reading. You’ll get insights into what makes Bolt tick, and how you can follow in its footsteps with the right taxi app development strategy!
What is Bolt?
Let’s keep it simple. Bolt is an app that helps people get around. Whether you want to book a ride, rent a scooter or car, or get food delivered, Bolt has you covered. The app started out as Taxify back in 2013, and today it’s giving giants like Uber a real challenge. With over 75 million users across 45+ countries, Bolt is a major player in the ride-hailing game.
Oh, and if you're dreaming of building your own taxi app, you might want to consider a Bolt clone. It’s a quick, smart way to launch your business with a tried-and-tested model. We’ll talk more about that later!
Some Facts & Timeline of Bolt
- Founders : Markus Villig
- Year founded : 2013
- Headquarter : Tallinn, Estonia
- Annual Revenue : €1.1 billion (2022)
- Area Served : 45 countries in Europe, Africa, Western Asia, Asia and Latin America, Portugal
Bolt Business Model
In more than 150 locations in Europe, Africa, Asia, North America, and a few places in South America, it provides on-demand ridesharing of scooters and other forms of transportation. Taxify was the previous name for Bolt. Markus Villig, who was 19 years old at the time, made it in 2013. With a loan of €5000 from his parents, he started his business. In August 2013, he successfully launched the company mTakso with the help of his parents and a developer. A year later, the company expanded internationally.
The use of ride-sharing or taxi apps has increased recently all around the world. The two most well-known businesses that provide this service are Uber and Bolt. The Bolt app, developed in 2013, started as a ride-sharing software for taxis but is now available in many countries for food delivery.
Google and Bolt started working together in February 2020. (last year). The worldwide pandemic had an impact on ride-sharing services. Bolt, on the other hand, was optimistic at the moment. Bolt has not undertaken any big layoffs or wage reductions, in contrast to Uber and other companies that have. Since owning a car is becoming less common, Bolt wants to find ways to get around that are better for the environment. A fresh service called Bolt Business Delivery was introduced in March 2020.
Bolt has become a significant player in the ride-hailing industry, and this blog post analyzes the business model that has contributed to its success. Delving into Bolt's pricing strategy, user experience focus, and driver incentives, the post provides valuable insights for entrepreneurs aspiring to enter the ride-hailing market. Understanding the intricacies of successful business models, as exemplified by Bolt, can guide businesses in developing strategies that resonate with both users and service providers.
Are you looking for a Bolt clone to create a white-label taxi booking app. An Bolt clone app solution allows you to deploy an application like Bolt in seconds. Sow the seed of investment in a Bolt app solution and enjoy the rewards of making a profit in the long run.
How Does Bolt Works?
Bolt uses an app-based mobility platform to offer taxis, food delivery, e-scooters, and car rentals in 150 cities. In collaboration with independent contractors, the business offers these services. The contractors work as needed because they are only paid after a project is finished.
Bolt collaborates with neighborhood restaurants and supermarkets, who in turn provide the contractors with food and beverages. The infrastructure is run by Bolt, who enables payments between clients and drivers who have accessible supplies. Together with vehicle hailing and food delivery, the app also allows users to rent electric bikes and scooters. Bolt Scooter Platform gives local businesses the infrastructure and stock they need to run their scooter fleets.
This franchise idea also works for Bolt's ride-hailing and food delivery services, which means that local business owners can work with Bolt to bring its products to their areas. Additionally, Bolt has created a software platform called Bolt Dispatcher that helps taxi companies manage their fleets more effectively. The Bolt app is available for download and works on tablets and smartphones running iOS and Android. Users can also access the service through a browser by using the Bolt Web App.
Also Read: Uber Business Model | How Uber Makes Money
How does Bolt Make Money
Bolt makes money by charging commissions, renting e-scooters and cars, paying for software subscriptions, and opening franchises. Bolt navigates a marketplace business approach with ease. Its marketplace must maintain a steady supply, in this case, restaurants and drivers, that meets the demand at the moment.
In the same way that every other ride-sharing service does, Bolt makes money by charging its users. It also offers meal delivery services and makes money from them. As a ride-sharing app, Bolt charges drivers a commission for each trip. Compared to other platforms that provide the same service, this is still 10% less.
Because of this price decrease, Bolt customers will pay less, and drivers will make more money. The company makes less money through commission since it was built from the beginning to be cost-effective. As a food delivery app, Bolt charges approximately Rs. 5 for excellent service from neighborhood restaurants. As a result of this, restaurants pay other aggregators between 25% and 35% less. Many local restaurants have joined the Bolt Food partner program because the platform has low delivery fees and is open to business.
Local businesses wishing to register on the platform will find the company to be the perfect fit because it runs on a reliable business model without any Chinese support. In the sections that follow, we'll look more closely at each source of income for the business.
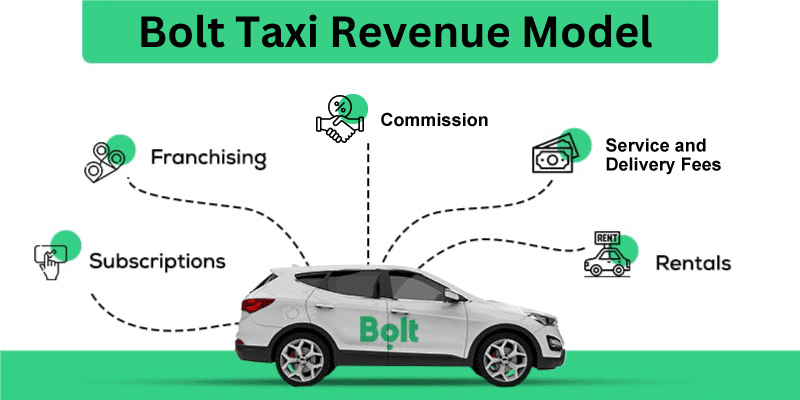
Subscriptions
By offering its dispatch software to taxi businesses, Bolt App makes a meager profit. Drivers can automatically allocate assignments based on their location and predefined wait times thanks to the software's capabilities. For the cab industry, having an Android and iOS app is also beneficial. Bolt (or, more precisely, Taxify) was inspired by the dispatch program. Each motorist back then had to pay a subscription fee of €12 to €15 per month. Most likely, the bolt pricing from before is still in place.
Franchising
Finally, Bolt generates revenue by franchising its technology to entrepreneurs, who then utilize it to start up regional ride-hailing businesses. Bolt's brand recognition and technological capabilities can be utilized by business owners thanks to the franchising model. Their time to market is significantly shortened as a result. Prospective partners must have the necessary financial resources and a local network to join.
It is logical to assume that Bolt and its franchisees have some sort of revenue-sharing structure, even though this is not publicized. This implies that a portion of the profits made by the local partner goes to the corporation.
Commissions
The various commission fees that Bolt charges drivers and restaurants account for the lion's share of its income. Drivers are paid a commission that ranges from 10% to 25% of the total cost of the order. Depending on where he is driving, the proportion changes dramatically. For each ride, Bolt levies a service fee of 10%. Bolt also charges delivery and payment processing fees so that it can pay its delivery staff and payment networks like Mastercard and Visa.
Service and delivery fees
Customers of Bolt are also charged a service fee to use its platform. No more than 10% of the entire fare is included in this fee. Depending on the customer's location, a delivery fee is also assessed for food orders. Food orders that are less expensive than the minimum order price are also subject to a minor order fee.
Rentals
Users of the Bolt app can rent e-scooters and other vehicles nearby in addition to placing food orders and calling for a cab using the app. Users using scooters must pay a €1 unlocking fee as well as an additional $0.15 for each minute of use. Consumers can pay a minute fee to the car firm (dubbed Bolt Drive). If the car is reserved for more than 15 minutes, there will also be a reservation fee.
Bolt is the owner and operator of the e-scooters and, possibly, the cars. As a result, the company keeps all earnings. Yet, running these kinds of businesses may be very expensive because they frequently need to replace damaged scooters and recharge them.
The sale of dispatch software to taxi firms is another revenue stream for Subscription Fee Bolt, albeit a small one. The software computes automated dispatch by taking a driver's position and a custom queue into account. Additionally, the business offers Android and iOS apps that aid taxi companies in gaining greater patronage. The dispatch software model served as the foundation for Bolt (or, more specifically, Taxify). It paid a monthly subscription fee for each driver in the system at the time that ranged from €12 to €15. Likely, the price system is still in place.
What are Bolt's funding and valuation
- According to Crunchbase, Bolt has raised $1.3 billion in debt and equity capital throughout the 12 rounds.
- D1, Creandum, Niya Capital, G Squared, and Sequoia Capital are a few notable investors.
- With a $713 million Series E investment in August 2021, Bolt is currently valued at $4.75 billion.
Also Read: Lyft Business Model: Disrupting The Ride-Sharing Industry
What is Bolt's revenue
According to Bolt's most recent financial information, the company generated €221 million in revenue in 2020, an increase of €73 million from €148 million in revenue the year before. In Tallinn, Estonia, Oliver Leisalu, Martin Villig, and Markus (CEO) founded Success Story of Bolt Bolt in 2013. From a young age, Markus was destined to become a digital entrepreneur. Most likely, his brother Martin had the most impact on him. He started as one of Skype's original workers and eventually launched his own company. While still in high school, Markus started his first business by creating websites for nearby companies. They found it difficult to order a cab in Tallinn, where they were based. Due to the city's shortage of operators, prices were high and lines were long.
Once known as mTakso, the company changed its name to Taxify and began acting as a cab aggregator. Markus was destined to be a technological entrepreneur from an early age. The most influential person in his life was probably his brother Martin. He was one of the first employees at Skype and later established his own business. Markus's first business was building websites for local businesses, which he did while he was still in high school.
Markus and Martin conceptualized Bolt while still in high school. They found ordering a cab in Tallinn, their base of operations, to be cumbersome. There were a limited number of operators in the city, resulting in high prices and long wait times. Markus used money that he borrowed from his parents to create the app's prototype. A few hundred taxi drivers in the area signed up for the launch of the app in August 2013.
How Can Appicial Help You in Taxi App Development
More than 200 business owners were assisted by Appicial in beginning their digital journeys. Are you wondering WHY Appicial should develop your taxi clone app? There are numerous benefits to using aPurple to digitize your taxi service or launch your own ride-sharing company rather than just one or two.
- Ready-To-Launch Taxi App: Among many other applications, we provide white label readymade clone scripts for taxi services like Bolt.
- In-House Team of Specialists: Professional designers and developers are on board for end-to-end support as part of an internal team of specialists.
- Affordability: Customized quotes to suit every client’s budget.
- Proven Expertise: We have deployed similar applications before. Who’s better than a clone app development company with top-quality experience?
FAQs
The Bolt business model shows how you can mix affordability, convenience, and innovation to disrupt the ride-hailing industry. As more startups look to build their own Bolt clone or Uber clone, the future of taxi app development looks bright. If you’re ready to take the plunge, now’s the perfect time to bring your idea to life!
Conclusion
Conventional ride-sharing services have been changed by the Bolt business model, which combines an on-demand transportation service with a peer-to-peer business model and a user-friendly platform for customers. It has established the industry standard and is well-positioned to continue to be a major player in the ride-sharing market. Customers can anticipate seeing more affordability, convenience, and safety and security features as more businesses attempt to replicate Bolt's success. Bolt and its competitors are ensuring that the future of ride-sharing services will be promising and bright by pushing the boundaries of innovation.
Looking out to start your own venture like Bolt? Try out our HireMe Taxi Bolt Clone, the easiest way to kick-start your taxi business.





